Introduction
Cloud technology has transformed the way we store, manage, and share data. From startups to global enterprises, almost every organization now relies on cloud platforms to operate efficiently and scale quickly. But as cloud adoption grows, so do security threats. Data breaches, misconfigurations, and unauthorized access are becoming common, and one weak control can compromise sensitive information.
Protecting your cloud environment requires more than just a strong password — it needs a comprehensive, proactive strategy that combines technology, policy, and human awareness. This article provides expert-approved, easy-to-understand cloud security tips to help you strengthen your data protection in 2025. Whether you use AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, or private cloud services, these practices will help safeguard your data, ensure compliance, and maintain customer trust.
Why Cloud Security Matters
Cloud computing offers scalability and convenience — but it also expands your attack surface. Understanding why security is crucial helps you approach it more seriously.
1. Data is your most valuable asset
Your business data includes financial records, customer information, intellectual property, and analytics. If stolen or leaked, it can cause financial losses, legal issues, and reputational harm.
2. Cyber threats are increasing
Hackers target cloud systems using methods like phishing, misconfigured APIs, weak passwords, or stolen tokens. Modern attacks are automated and exploit minor vulnerabilities at scale.
3. Shared responsibility model
Cloud security is not entirely managed by the provider. The provider protects infrastructure, but you are responsible for securing your data, users, and configurations. Ignoring this model often leads to breaches.
4. Regulations demand protection
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and e-commerce must comply with data protection laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Failure to do so can lead to fines and loss of credibility.
5. Complex environments need visibility
Modern cloud infrastructures are dynamic — servers spin up and down automatically, workloads shift between regions, and APIs connect various services. Without clear visibility, securing every element is difficult.
15 Proven Cloud Security Tips for 2025
Here are the most important, practical, and user-friendly cloud security tips based on expert guidance and industry best practices.
1. Understand the Shared Responsibility Model
Every major cloud provider follows this model. They secure the infrastructure, while you must secure your applications, data, and user access. Make sure your team knows which tasks fall on your side — such as access control, data encryption, and backup management.
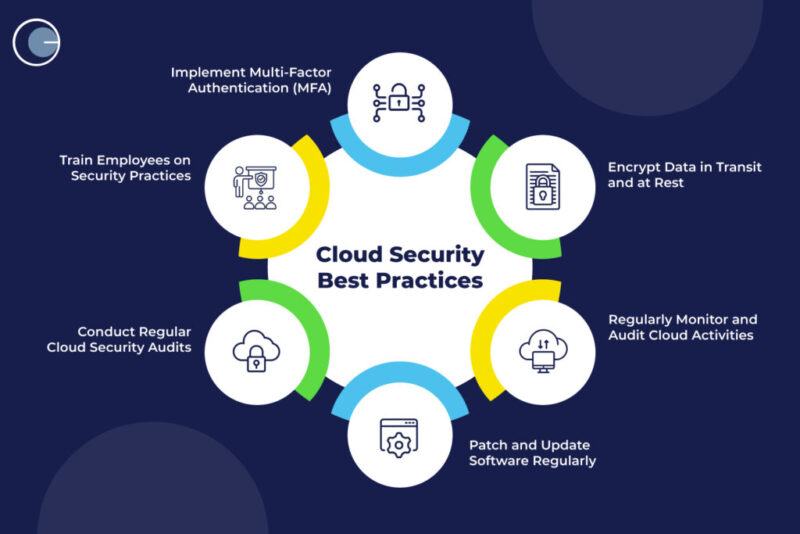
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere
Passwords alone are no longer enough. Enabling MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring another verification step, such as a phone code or hardware token. This simple step can block over 90% of account-based attacks.
3. Follow the Principle of Least Privilege
Only give users and systems the permissions they absolutely need. Over-privileged accounts are a major cause of insider breaches. Regularly audit permissions and remove unnecessary access.
4. Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Encryption keeps data unreadable to unauthorized users. Always encrypt stored files (“at rest”) and use secure protocols like HTTPS or TLS when transmitting data (“in transit”). For maximum security, manage your own encryption keys if possible.
5. Protect and Rotate Access Keys
API keys, SSH keys, and credentials should be stored securely and rotated regularly. Avoid embedding them in code or storing them in shared documents. Use a secret management service to automate key rotation.
6. Audit and Monitor Configurations
Regularly scan your cloud setup for misconfigurations — such as open storage buckets or public databases. Many breaches happen because of a single forgotten setting. Continuous monitoring tools can help identify and fix these weaknesses early.
7. Use Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools
CSPM tools automatically check your cloud environments for compliance and vulnerabilities. They monitor identity settings, encryption, networking rules, and report misconfigurations before attackers find them
8. Conduct Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Scans
Simulating attacks on your system helps you find weak spots before real hackers do. Regular penetration testing, combined with automated vulnerability scans, ensures your defenses remain strong even as your infrastructure evolves.
9. Strengthen Network Boundaries
Use virtual private clouds (VPCs), firewalls, and segmentation to isolate workloads. Limit public exposure by keeping sensitive systems within private networks. Define clear inbound and outbound traffic rules.
10. Avoid Unnecessary Public Exposure
Never make databases or storage buckets public unless required. Restrict access to trusted IP addresses or private connections. Publicly exposed assets are the easiest targets for cybercriminals.
11. Implement a Zero-Trust Security Model
Zero Trust means “never trust, always verify.” Every access request — even from inside your network — should be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated. This reduces the chance of attackers moving laterally once they gain access.
12. Enable Continuous Logging and Monitorin
Collect and review logs for all activities, especially admin actions and API calls. Enable alerts for unusual behavior, such as failed login attempts or unauthorized changes. Centralized logging also simplifies audits and investigations.
13. Train Employees on Cloud Security Awareness
Human error remains the biggest security risk. Regular training helps employees identify phishing, use secure passwords, and understand data handling procedures. Developers should also follow secure coding guidelines for cloud applications.
14. Maintain Backups and Disaster Recovery Plan
Backups protect your business from ransomware, accidental deletion, or system failure. Store backups in separate, secure locations and test recovery procedures regularly. Automate backups to ensure consistency.
15. Stay Compliant and Review Certifications
Choose providers that meet recognized security standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, or FedRAMP. Review compliance requirements for your region and industry. Regular audits help you stay aligned with legal and regulatory demands.
How to Build a Practical Cloud Security Roadma
To apply these tips effectively, follow a structured approach:
Step 1: Assess Your Current State
Start by identifying what you already have in the cloud — data types, users, configurations, and existing controls. This helps you find gaps.
Step 2: Prioritize Critical Risks
Focus first on areas that have the highest impact, such as identity access management, encryption, and backups.
Step 3: Implement Quick Wins
Turn on MFA, close public ports, enable encryption, and audit permissions. These simple changes dramatically improve your security posture.
Step 4: Automate and Monitor
Introduce CSPM or SIEM tools to monitor configurations, detect anomalies, and generate alerts automatically.
Step 5: Create a Security Culture
Encourage your team to treat security as everyone’s responsibility. Regularly update policies, review access, and discuss lessons learned from incidents.
Emerging Cloud Security Trends for 2025
- AI-Driven Threat Detection – Artificial intelligence and machine learning are now used to identify anomalies in real time, improving detection accuracy.
- Shift-Left Security – Integrating security early in the development cycle ensures that vulnerabilities are caught before deployment.
- Container and Kubernetes Security – As more workloads move to containers, securing cluster configurations and secrets becomes critical.
- Zero-Trust Adoption – Organizations are rapidly adopting Zero-Trust frameworks to mitigate insider and external risks.
- Data Sovereignty and Privacy – With evolving global laws, companies must know where data is stored and processed to stay compliant.
Staying updated with these trends helps organizations remain resilient in an evolving cyber landscape.
Common Cloud Security Mistakes to Avoid
- Leaving storage buckets or databases publicly accessible
- Using weak or reused passwords for admin accounts
- Ignoring software updates and patches
- Failing to review IAM roles regularly
- Skipping data encryption or relying on defaults
- Overlooking employee training and awareness
- Not monitoring third-party integrations
Avoiding these mistakes can prevent many common security incideRead more
Read more: G15Tools.com Gadget Review – Features, Uses, and Honest User
Conclusion
Cloud technology delivers unmatched flexibility and innovation, but without strong security, it becomes a liability. Protecting your cloud data requires continuous attention, layered defenses, and a well-trained team. Start with essentials like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and least privilege access, then expand into monitoring, automation, and Zero-Trust principles.
Remember — security is not a one-time task; it’s a process of ongoing vigilance and improvement. By following the tips in this guide, you can reduce risk, maintain compliance, and build trust with your users and customers. In 2025 and beyond, cloud security isn’t just about protection — it’s about enabling safe, confident growth.
FAQs
1. What are the best ways to secure cloud data?
Use strong encryption, enforce multi-factor authentication, apply least privilege access, and continuously monitor for unusual activity.
2. Why is cloud security important in 2025?
As more businesses move to the cloud, threats are becoming more sophisticated. Strong security ensures data privacy, compliance, and trust.
3. How can I protect my cloud account from hackers?
Enable MFA, use complex passwords, review access permissions regularly, and avoid using shared credentials.
4. What is the shared responsibility model in cloud computing?
It defines which security tasks belong to the provider (infrastructure) and which belong to the customer (data, applications, access control).
5. How often should I audit my cloud security setup?
Perform continuous automated monitoring and full audits at least once every quarter or after major changes in infrastructure.